Want to boost your sperm count without making drastic lifestyle changes? You’d be surprised by how simple it can be. By tweaking your diet and incorporating a few healthy habits, you can naturally increase your sperm production. Let’s dive into some easy, effective ways to boost your sperm count and improve overall reproductive health.
1. Eat a Sperm-Friendly Diet
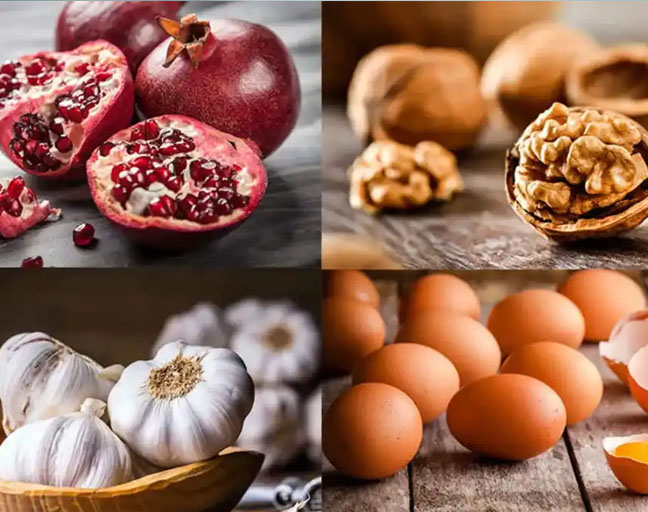
A poor diet is often behind fertility struggles. To help your body produce more sperm, opt for whole, unprocessed foods like fresh fish, lean meats, nuts, and a variety of vegetables. Foods like broccoli, asparagus, and citrus fruits pack a punch when it comes to supporting sperm health. You should also limit exposure to heavy metals and drink green tea for its energizing and blood circulation-boosting benefits.
Micronutrients like vitamins, amino acids, and trace elements play a crucial role in improving sperm quality. Here are some foods you should definitely add to your diet:
- Dark Chocolate: Not just a treat! It contains L-Arginine, which can improve sperm count and enhance your libido. But remember, moderation is key to avoid extra calories.
- Oysters: These are packed with zinc, which boosts testosterone levels and, in turn, improves sperm quality and libido.
- Eggs: Rich in vitamin E and protein, eggs are essential for strong, healthy sperm and help combat free radicals that can damage them.
- Bananas: Packed with bromelain, bananas can increase libido and stamina. Plus, the vitamin B they contain is fantastic for overall energy levels.
- Spinach: This leafy green is full of folic acid, which helps protect sperm cells from damage and supports healthy sperm development.
- Garlic: Known for its medicinal properties, garlic boosts sperm volume and acts as an aphrodisiac, thanks to the compound allicin.
- Asparagus: A powerhouse of vitamin C, asparagus helps protect sperm from free radical damage and improves overall sperm health.
- Walnuts: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, walnuts help increase sperm count and promote better blood circulation, which is key for sexual health.
- Carrots: Full of vitamin A, carrots help improve sperm motility and production, ensuring your sperm are ready for action.
- Pumpkin Seeds: These seeds are great for triggering testosterone production and improving both sperm count and semen volume.
2. Keep Things Cool
Sperm production thrives in cooler conditions, typically between 29°C and 35°C. If the temperature in your testicles goes above 36°C, sperm production slows down. That’s why it’s important to avoid unnecessary heat around your groin area.
Here are some tips to keep things cool:
- Avoid wearing tight-fitting clothes and never place laptops directly on your lap.
- Say no to long sauna or tanning sessions.
3. Get Enough Sleep and Exercise
Sleep isn’t just about feeling rested—it’s crucial for boosting your sperm production. During REM sleep, testosterone levels rise, which is essential for healthy sperm. Aim for at least 7 hours of quality sleep each night.
Exercise is equally important. High-intensity workouts, like squats, deadlifts, and pull-ups, can help increase testosterone levels and improve your overall sexual health. Engaging large muscle groups is the key to maximizing these benefits.
4. Masturbate Less
While masturbation is natural, too much of it can affect sperm production. A healthy male can release 300-500 million sperm during ejaculation, but only a fraction survive in the vagina. Let your sperm mature, and focus more on intimacy with your partner to stimulate sperm production.
5. Keep Your Phone Away
Some studies suggest that electromagnetic radiation from mobile phones can negatively affect sperm health. To be safe, keep your phone out of your pants pocket—use a jacket pocket instead.
6. Avoid Toxins
Your sperm health can suffer from toxins found in alcohol, cigarettes, and illicit drugs. These can lower your libido and reduce blood flow to your penis. Additionally, steer clear of exposure to heavy metals, lead, and chemical solvents, as they can damage sperm.
7. Consider Taking Fertility Supplements
If you’re looking to give your sperm health an extra boost, fertility supplements might help. Look for supplements containing vitamins B, C, D, E, as well as zinc and folic acid. These nutrients can enhance sperm quality and motility.
8. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying excess weight can impact your libido and reduce sperm production. Staying active and eating a balanced diet can help you maintain a healthy weight, which in turn supports your reproductive health.
With these simple tips, you’ll be on your way to increasing your sperm count and improving overall sexual health. The key is consistency—so make these changes a regular part of your routine, and soon enough, you’ll notice the benefits.