You might have heard the term “prostate” before, but do you really know what it does? Most people don’t fully understand this little gland and its big impact on men’s health. So, what exactly does the prostate do? It plays a key role in male reproductive health, and keeping it in good shape is essential if you want to avoid potential fertility issues down the road.
Understanding the Prostate
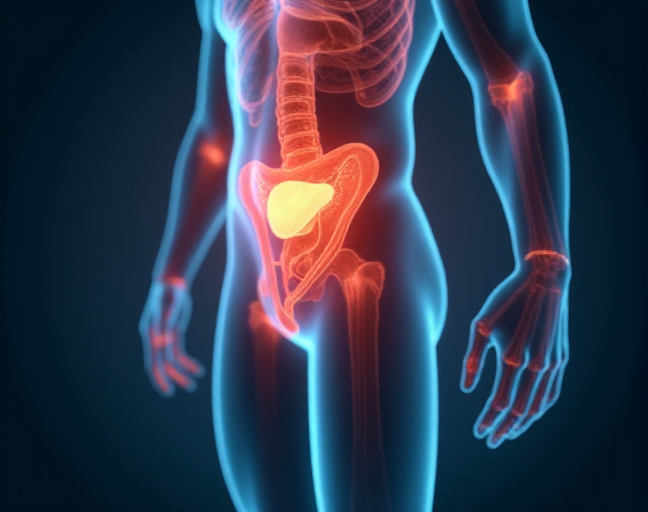
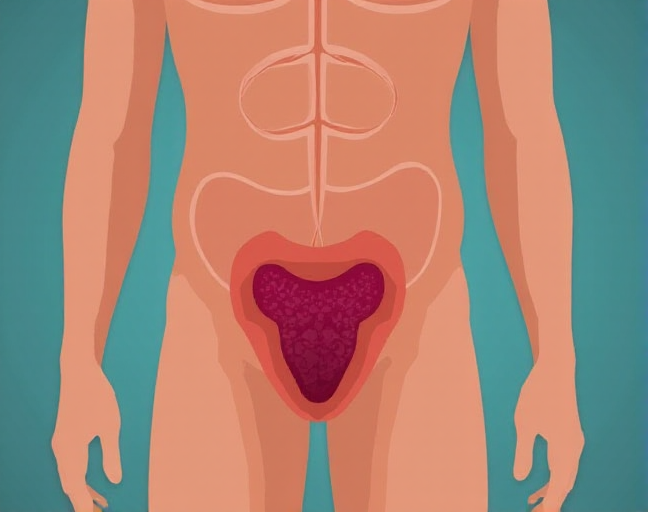
The prostate is a small gland found only in men, about the size of a walnut. It sits just below the bladder, right in front of the rectum. The male urethra, which is the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, passes right through the middle of the prostate. As you age, especially between 40 and 50, the prostate can grow larger, which may affect your ability to urinate.
Unlike the testes or penis, you can’t physically feel or see the prostate. A doctor can check its size and condition with a simple digital rectal exam (DRE).
What Does the Prostate Actually Do?
The prostate has three major functions:
- Urinary Control: The prostate surrounds the urethra, and its muscles gently squeeze it to help control urine flow.
- Semen Production: The prostate also contributes to semen production. It produces about 80% of the fluid in semen, which mixes with sperm from the testicles. This fluid nourishes the sperm and helps it travel. Just above the prostate are the seminal vesicles, which store the sperm and fluids before ejaculation.
- Hormonal Regulation: Lastly, the prostate plays a role in male hormone metabolism. Testosterone, the primary male hormone, is converted into its more active form—dihydrotestosterone (DHT)—within the prostate.
How to Keep Your Prostate Healthy
Now that you understand the prostate’s role, you’re probably wondering how to take care of it. After all, it’s an important gland, and it can cause problems, especially as men age. Prostate issues like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and even prostate cancer become more common after age 50, with African-American men and those with a high-fat diet being at higher risk.
Here’s how you can take action to keep your prostate in tip-top shape:
- Get Regular Blood Tests: You can check for potential prostate problems with a blood test called the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test. This test can spot signs of prostate enlargement or even early-stage prostate cancer before symptoms appear. Make it a habit to check your PSA levels every year.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): This simple, quick exam by a doctor can help determine the size of your prostate and detect any irregularities that could suggest cancer. Both the PSA test and the DRE are essential for catching potential issues early.
- Check Your Family History: Prostate cancer often runs in families. If your father or brother had prostate cancer, you should be extra vigilant and get regular screenings.
- Eat Healthy: While there’s no clear-cut evidence that eating certain foods can prevent prostate issues, a diet rich in vegetables, antioxidants, and low in animal fats is generally considered good for prostate health. Men in countries like Japan, who eat less animal fat, tend to have a lower rate of prostate cancer.
- Try Herbal Supplements: Some herbal remedies, like saw palmetto, may help alleviate symptoms of prostate problems. It’s believed to help relax the prostate, easing symptoms.
- Relax and Stress Less: Stress can affect your overall health, including your prostate. In fact, 1 in 6 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime, but only 3 out of 100 will die from it. Prostate cancer often grows slowly, and if it’s not aggressive, there’s no need to panic.
- Exercise Regularly: Staying active is good for your body, and it can benefit your prostate as well. Research suggests that moderate exercise can help maintain prostate health.
- Do Kegel Exercises: Yes, men can benefit from Kegel exercises, too! These exercises target your pelvic floor muscles and can help reduce urine leakage, a common issue for men with prostate problems.
Taking care of your prostate is all about maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying proactive with screenings, and being mindful of your family history. Keeping these tips in mind can help ensure your prostate stays healthy for years to come.