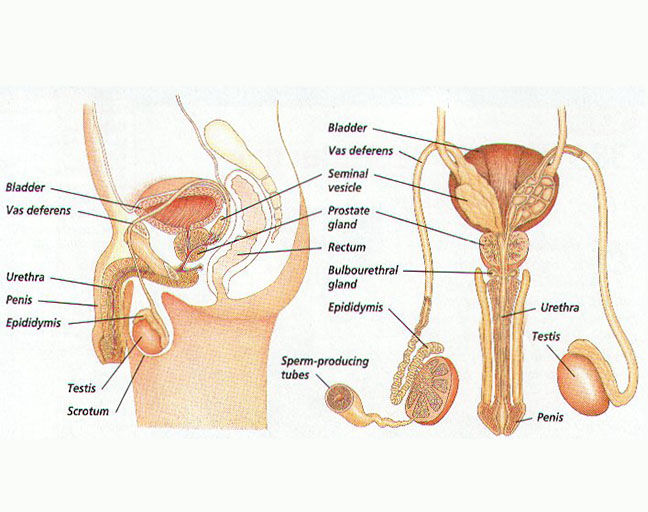
Testosterone is a key hormone in the male body, influencing everything from muscle growth and bone density to libido. Produced primarily in the testicles, it plays a vital role in reproductive health. As you age, typically after 30, your testosterone levels naturally start to decline. This drop can lead to several health issues, leaving many men wondering how to get those levels back up. Luckily, there are simple, natural ways to help boost testosterone, so let’s dive into some easy strategies that could make a difference.
Quick and Easy Ways to Boost Your Testosterone
Your daily habits, especially your diet and lifestyle, can have a significant impact on your testosterone levels. Here’s how you can start making changes right now:
1. Prioritize Sleep
Let’s face it—there’s nothing more crucial than a good night’s sleep when it comes to maintaining testosterone. Skimping on sleep can throw your hormonal balance off, so aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. This is when your body gets a chance to repair and regenerate, including releasing important hormones like testosterone. Simply put, sleep is the foundation of your health.
2. Keep Your Weight in Check
Carrying extra weight can wreak havoc on your testosterone. Obesity is a major factor in lowering T-levels, so shedding those excess pounds could help you bring them back up. But don’t go to extremes—being underweight can also negatively impact testosterone production. Aim for a healthy, balanced weight to keep things running smoothly.
3. Stay Active
To boost testosterone, staying active is essential. A sedentary lifestyle sends a message to your body that it doesn’t need to strengthen bones and muscles, which ultimately results in lower testosterone levels. You don’t need to hit the gym for hours; even a 10-20 minute walk every day can make a big difference. Weight training is another great way to raise testosterone, but don’t overdo it—too much exercise can raise stress hormones, which have the opposite effect on T-levels.
4. Manage Stress Effectively
Stress is unavoidable in today’s fast-paced world, but learning to manage it can go a long way in boosting testosterone. Chronic stress raises cortisol levels in the body, and high cortisol can inhibit testosterone production. Try to avoid long working hours and engage in activities you enjoy to de-stress. Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques can also help you keep stress in check.
5. Review Your Medications
Certain medications can negatively affect your testosterone levels. Drugs like opioids, glucocorticoids, and anabolic steroids are common culprits. Don’t stop taking any medications without consulting your doctor, but if you think they’re impacting your hormone levels, work with your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan.
6. Balance Your Diet
For testosterone production, a balanced intake of fats, proteins, and carbs is essential. Protein helps you build muscle and burn fat, while healthy carbs fuel your workouts. However, be cautious about overeating or extreme dieting, as this can affect your weight and, in turn, your testosterone levels. Whole foods like lean meats, vegetables, and whole grains are your best bet for maintaining that balance.
7. Cut Back on Sugar
While it’s important to get the right amount of carbs, it’s also critical to watch your sugar intake. Excess sugar spikes insulin, which can suppress testosterone levels. Plus, too much sugar is stored as fat, which absorbs testosterone and limits what’s available for your muscles and bones. Stick to whole grains, fruits, beans, and oatmeal for your carb fix, and steer clear of processed sugary foods.
8. Add Zinc to Your Diet
Zinc is crucial for testosterone production, and you can find it in dairy, meats, and fish. Make sure you don’t overcook your meat or fish, as this can diminish its zinc content. If you don’t get enough zinc from food, consider a supplement, but be careful not to exceed 40mg, as higher doses can lead to nausea.
9. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol, especially beer, can negatively affect testosterone levels. Beer contains estrogenic compounds that can increase your estrogen levels and lower your testosterone. While it’s best to quit drinking altogether, at least try to limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels to protect your T-levels.
Foods That Naturally Boost Testosterone
Certain foods can give your testosterone a natural boost. Here’s a breakdown of some of the best options:
- Bananas: Bananas contain bromelain, an enzyme that helps boost libido and testosterone levels. Plus, they provide B-vitamins like riboflavin, which support testosterone production.
- Fish Oil: Fish oil, especially from fatty fish like salmon and tuna, can help stimulate the production of luteinizing hormone, which, in turn, boosts testosterone. It also reduces globulin activity, which can lower testosterone levels.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Veggies like broccoli, cauliflower, and kale can help lower estrogen levels in your body, making free testosterone more available. They’re also rich in fiber, which helps with weight management, indirectly boosting testosterone levels.
By incorporating these foods and lifestyle changes into your routine, you can naturally increase your testosterone and improve your overall health. The key is consistency and balance—small adjustments to your daily habits can lead to big results over time.